Tax treaties provide established frameworks for avoiding double taxation and resolving disputes between countries, ensuring clarity and predictability for international investors. In contrast, DeFi tax harmonization aims to create unified tax rules across jurisdictions, addressing the decentralized and borderless nature of blockchain transactions for consistent compliance. Harmonizing DeFi taxation could simplify reporting, reduce regulatory arbitrage, and enhance transparency in cross-border digital asset investments.
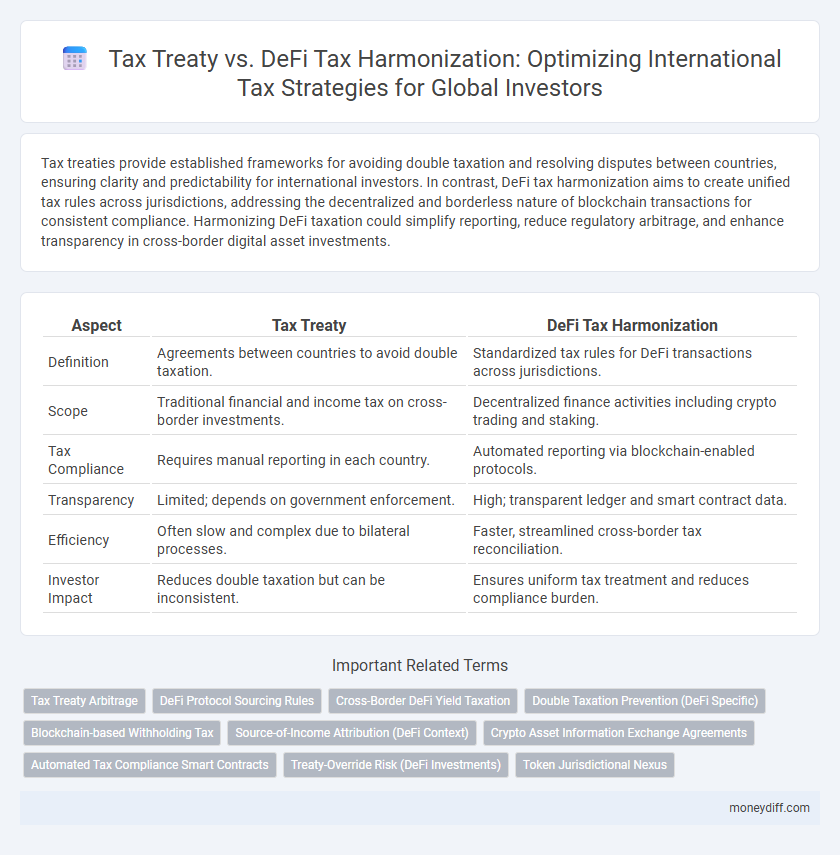
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tax Treaty | DeFi Tax Harmonization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreements between countries to avoid double taxation. | Standardized tax rules for DeFi transactions across jurisdictions. |
| Scope | Traditional financial and income tax on cross-border investments. | Decentralized finance activities including crypto trading and staking. |
| Tax Compliance | Requires manual reporting in each country. | Automated reporting via blockchain-enabled protocols. |
| Transparency | Limited; depends on government enforcement. | High; transparent ledger and smart contract data. |
| Efficiency | Often slow and complex due to bilateral processes. | Faster, streamlined cross-border tax reconciliation. |
| Investor Impact | Reduces double taxation but can be inconsistent. | Ensures uniform tax treatment and reduces compliance burden. |
Understanding Tax Treaties: A Foundation for Global Investors
Tax treaties establish crucial guidelines that prevent double taxation and allocate taxing rights between countries, enabling global investors to navigate cross-border income efficiently. These agreements provide clarity on tax residency, withholding rates, and income classification, reducing risks of disputes and excessive taxation. Understanding tax treaties forms a foundational strategy for investors dealing with international assets before integrating complex DeFi tax harmonization frameworks.
DeFi Tax Harmonization Explained: Bridging Jurisdictions
DeFi tax harmonization aims to create a standardized framework for tax reporting and compliance across multiple jurisdictions, addressing the complexities of decentralized finance transactions. Unlike traditional tax treaties that rely on bilateral agreements between countries, DeFi tax harmonization leverages blockchain technology to provide transparent and automated tax data sharing. This approach reduces tax evasion risks and enhances international cooperation by aligning tax obligations with the decentralized nature of DeFi platforms.
Key Differences Between Traditional Tax Treaties and DeFi Tax Frameworks
Traditional tax treaties primarily establish bilateral agreements between countries to prevent double taxation and facilitate cross-border investment by defining taxing rights and dispute resolution mechanisms. In contrast, DeFi tax frameworks focus on harmonizing decentralized finance transactions through automated, blockchain-based reporting and compliance, emphasizing transparency and real-time tax calculation across multiple jurisdictions. Key differences include the centralized enforcement and fixed treaty terms in traditional treaties versus the algorithm-driven, dynamic, and decentralized protocol-based nature of DeFi tax integration.
Implications for Cross-Border Investment Returns
Tax treaties provide established frameworks that mitigate double taxation and clarify residency status for cross-border investors, ensuring predictable tax liabilities. DeFi tax harmonization aims to standardize decentralized finance regulations globally, reducing compliance complexity and enhancing transparency in international transactions. Harmonized DeFi tax protocols could significantly improve cross-border investment returns by minimizing tax inefficiencies and fostering investor confidence in decentralized markets.
Reporting Requirements: Tax Treaty vs. DeFi Ecosystems
Tax treaties establish clear reporting requirements between jurisdictions to prevent double taxation and ensure transparency in cross-border investments, often mandating detailed disclosures of income and asset holdings. DeFi ecosystems, however, face challenges in tax harmonization due to decentralized, pseudonymous transactions that complicate consistent reporting standards and compliance enforcement across borders. Harmonizing tax reporting in DeFi requires developing interoperable frameworks that align with international tax treaties while accommodating blockchain's unique attributes to enhance transparency and reduce tax evasion risks.
Double Taxation Risks and Relief Mechanisms
Tax treaties play a critical role in mitigating double taxation risks for international investors by providing clear relief mechanisms, such as tax credits and exemptions, thereby reducing fiscal barriers across jurisdictions. In contrast, DeFi tax harmonization seeks to create standardized tax rules within decentralized finance platforms to address the complexities and inconsistencies in cross-border taxation of crypto assets. Effective coordination between tax treaties and DeFi tax frameworks is essential to ensure comprehensive double taxation relief and enhance compliance in international investment portfolios.
Compliance Challenges in DeFi-Driven International Investing
Tax treaties provide structured frameworks for avoiding double taxation and ensuring compliance in cross-border investments, but they often lag behind the rapid innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi tax harmonization efforts aim to establish standardized reporting and compliance mechanisms to address the transparency and jurisdictional challenges intrinsic to blockchain transactions. Navigating compliance in DeFi-driven international investing requires investors to reconcile traditional treaty obligations with dynamic regulatory requirements and real-time transaction data on decentralized networks.
Future Trends: Will DeFi Inspire Global Tax Harmonization?
Tax treaties currently provide a framework for avoiding double taxation in international investing, but their complexity and bilateral nature limit adaptability to DeFi's decentralized environment. DeFi tax harmonization efforts aim to standardize reporting and compliance through blockchain transparency, potentially simplifying cross-border tax enforcement. Emerging trends suggest that DeFi's programmable standards could inspire multilateral tax frameworks, promoting global tax harmonization by enabling real-time, automated tax data exchange and consistent regulatory oversight.
Strategic Tax Planning: Choosing Treaties or DeFi Solutions
Strategic tax planning for international investing requires analyzing the benefits of tax treaties versus decentralized finance (DeFi) tax harmonization to optimize tax liabilities and compliance. Tax treaties provide established bilateral frameworks that reduce double taxation and clarify reporting obligations, while DeFi solutions offer innovative, real-time transparency and automation in cross-border tax calculations. Investors should assess the regulatory environment, transaction volumes, and jurisdictional risks to determine whether traditional treaty advantages or emerging DeFi tax protocols align better with their global investment strategies.
Practical Steps for International Investors Navigating Tax Complexity
International investors should prioritize understanding existing tax treaties between their home country and the countries where DeFi platforms operate to optimize tax obligations and avoid double taxation. Leveraging tax treaty provisions can provide clarity on residency, income sourcing, and withholding rates, which differs significantly from the currently fragmented DeFi tax regulations. Consulting cross-border tax professionals and utilizing advanced tax compliance software tailored for DeFi transactions are practical steps to harmonize tax reporting and ensure compliance in the evolving decentralized investment landscape.
Related Important Terms
Tax Treaty Arbitrage
Tax treaty arbitrage exploits differences between countries' tax treaties to minimize international tax liabilities, often creating complex compliance challenges for investors engaging in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. Harmonizing DeFi tax regulations across jurisdictions could reduce arbitrage opportunities, enhance transparency, and ensure consistent tax treatment for cross-border digital asset investments.
DeFi Protocol Sourcing Rules
DeFi protocol sourcing rules significantly impact the application of tax treaties by determining the jurisdictional source of income generated through decentralized finance platforms, affecting cross-border tax liabilities. Harmonizing these rules internationally ensures consistent tax treatment, reduces double taxation risks, and enhances compliance transparency for global DeFi investors.
Cross-Border DeFi Yield Taxation
Tax treaties provide structured bilateral agreements that reduce double taxation and clarify tax obligations for cross-border DeFi yield earnings, ensuring compliance with established international tax frameworks. DeFi tax harmonization seeks to standardize reporting and taxation rules across jurisdictions, addressing the complexities and inconsistencies in tracking decentralized finance income streams for international investors.
Double Taxation Prevention (DeFi Specific)
Tax treaties play a crucial role in preventing double taxation by clearly defining taxing rights between countries, whereas DeFi tax harmonization seeks to establish decentralized protocols that automate compliance and reporting across jurisdictions. Incorporating real-time blockchain data into international tax frameworks can enhance transparency and accuracy, addressing the unique challenges of double taxation in cross-border DeFi investments.
Blockchain-based Withholding Tax
Tax treaties provide bilateral agreements that reduce or eliminate withholding tax on cross-border income, enhancing certainty and compliance for international investors. Blockchain-based withholding tax solutions in DeFi enable real-time, automated tax collection and reporting, promoting tax harmonization and reducing evasion risks in decentralized finance environments.
Source-of-Income Attribution (DeFi Context)
Tax treaties provide clear guidelines for attributing source-of-income in traditional cross-border investments, reducing double taxation through established rules between jurisdictions. In contrast, DeFi tax harmonization faces challenges in source-of-income attribution due to decentralized transaction chains and lack of centralized intermediaries, requiring innovative regulatory frameworks to accurately identify taxable jurisdictions in international decentralized finance investments.
Crypto Asset Information Exchange Agreements
Tax treaties provide bilateral frameworks to avoid double taxation and ensure clarity on cross-border crypto asset transactions, while DeFi tax harmonization seeks uniform international standards for reporting and taxing decentralized finance activities. Crypto Asset Information Exchange Agreements enable authorities to share detailed transaction data, enhancing transparency and compliance in global crypto investing.
Automated Tax Compliance Smart Contracts
Automated tax compliance smart contracts leverage blockchain technology to enforce tax treaty provisions and DeFi tax harmonization, ensuring real-time, accurate tax reporting for international investments. These smart contracts reduce administrative burdens by automatically calculating and remitting cross-border taxes according to jurisdiction-specific rules within decentralized finance platforms.
Treaty-Override Risk (DeFi Investments)
Tax treaty provisions often lack clarity in addressing decentralized finance (DeFi) transactions, increasing treaty-override risk for international investors exposed to cross-border digital asset activities. The absence of harmonized DeFi tax regulations results in inconsistent treaty interpretations, potentially leading to double taxation or disputes over residency and source income allocation.
Token Jurisdictional Nexus
Tax treaties establish clear guidelines for determining tax jurisdiction and avoiding double taxation in cross-border investments, providing certainty for traditional financial assets. DeFi tax harmonization faces challenges in defining token jurisdictional nexus due to the decentralized nature of blockchain networks, requiring new frameworks to attribute tax obligations based on token origin, holder location, and transaction context.
Tax Treaty vs DeFi Tax Harmonization for International Investing Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com