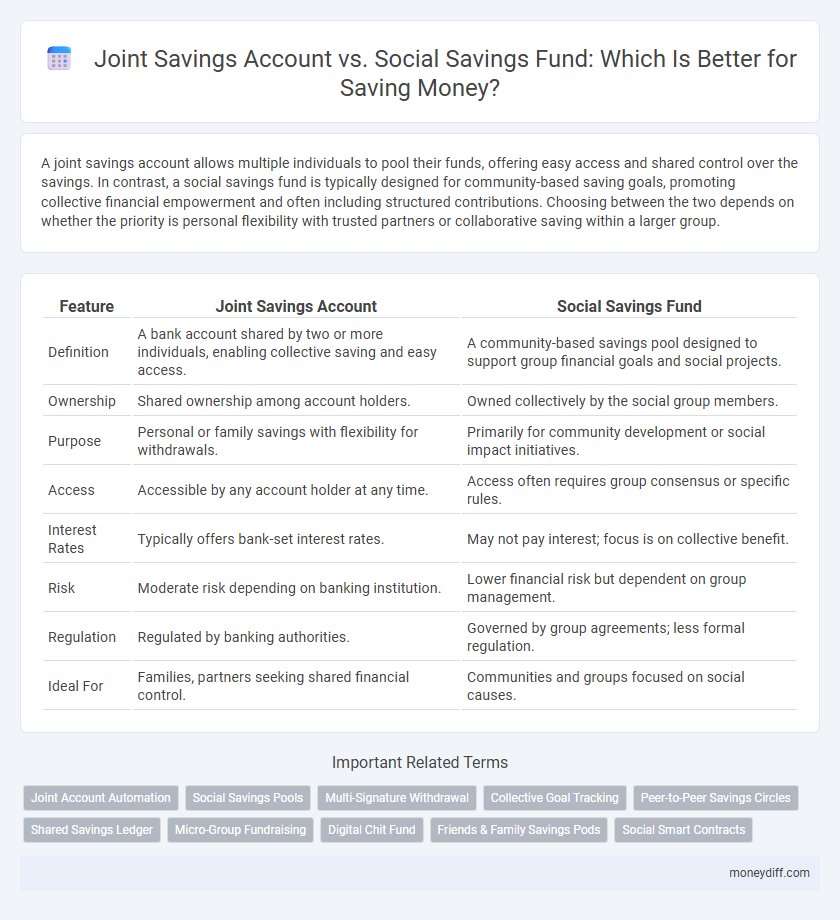
A joint savings account allows multiple individuals to pool their funds, offering easy access and shared control over the savings. In contrast, a social savings fund is typically designed for community-based saving goals, promoting collective financial empowerment and often including structured contributions. Choosing between the two depends on whether the priority is personal flexibility with trusted partners or collaborative saving within a larger group.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Joint Savings Account | Social Savings Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A bank account shared by two or more individuals, enabling collective saving and easy access. | A community-based savings pool designed to support group financial goals and social projects. |
| Ownership | Shared ownership among account holders. | Owned collectively by the social group members. |
| Purpose | Personal or family savings with flexibility for withdrawals. | Primarily for community development or social impact initiatives. |
| Access | Accessible by any account holder at any time. | Access often requires group consensus or specific rules. |
| Interest Rates | Typically offers bank-set interest rates. | May not pay interest; focus is on collective benefit. |
| Risk | Moderate risk depending on banking institution. | Lower financial risk but dependent on group management. |
| Regulation | Regulated by banking authorities. | Governed by group agreements; less formal regulation. |
| Ideal For | Families, partners seeking shared financial control. | Communities and groups focused on social causes. |
Understanding Joint Savings Accounts
A Joint Savings Account is a bank account shared by two or more individuals allowing all parties equal access to deposits and withdrawals, providing convenience for managing shared expenses or saving toward common goals. These accounts typically offer competitive interest rates and come with features like electronic transfers, ATM access, and unified account statements, ensuring transparent financial tracking for all holders. Understanding the terms regarding account ownership, liability, and withdrawal rights is crucial to adequately protect savings and maintain trust among joint account holders.
What Is a Social Savings Fund?
A Social Savings Fund is a community-driven financial pool where members contribute regularly to support collective goals or emergencies, fostering trust and mutual aid. Unlike a Joint Savings Account held by specific individuals, this fund emphasizes group participation and social impact, often managed through cooperative agreements. It leverages the power of social networks to encourage disciplined savings and financial inclusion within communities.
Key Differences: Joint Account vs Social Savings Fund
A joint savings account allows multiple account holders to deposit and withdraw money, providing shared access and responsibility over the funds, typically suited for families or business partners. A social savings fund pools contributions from a community or group to achieve collective financial goals, often used in microfinance or cooperative settings with a focus on social impact. Key differences include ownership structure, access to funds, and the primary objective, with joint accounts emphasizing shared control and social savings funds fostering collective savings and community investment.
Advantages of Joint Savings Accounts
Joint savings accounts offer shared access and management of funds, making them ideal for couples, families, or business partners who want transparent, collaborative saving. These accounts often provide easier fund transfers and bill payments, while fostering mutual financial goals and accountability. Compared to social savings funds, joint accounts typically feature more flexible withdrawal options and personalized control over the savings.
Benefits of Social Savings Funds
Social Savings Funds offer greater flexibility by allowing group contributions and fostering collective financial discipline, which enhances savings growth through pooled resources. These funds often provide higher interest rates compared to individual joint savings accounts, maximizing returns for participants. Additionally, Social Savings Funds promote community support and shared financial goals, increasing motivation and accountability among members.
Risks and Drawbacks of Joint Savings Accounts
Joint savings accounts expose account holders to risks such as loss of individual control over funds, as any account holder can withdraw money without the consent of others. The shared nature of the account creates potential conflicts and legal complications if one party incurs debt or financial disputes arise. Unlike social savings funds, joint accounts lack structured governance and safeguards, increasing vulnerability to mismanagement and fraud.
Challenges Associated with Social Savings Funds
Social savings funds often face challenges such as limited accessibility due to complex enrollment processes and regulatory restrictions that hinder quick withdrawals. These funds may also lack personalized control over individual contributions compared to joint savings accounts, reducing flexibility for members. Moreover, social savings funds can encounter difficulties in maintaining transparency and trust among participants, which impacts long-term sustainability.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Each Option?
Joint savings accounts suit couples, family members, or business partners needing shared access and easier management of pooled funds for common expenses or goals. Social savings funds are ideal for community groups or individuals seeking collective savings with social objectives, promoting financial inclusion and mutual support through regular contributions. Each option aligns with different financial needs: joint accounts focus on shared ownership and liquidity, while social savings emphasize group accountability and social impact.
Security and Access: Protecting Your Savings
A joint savings account offers secure, shared access with multiple account holders able to monitor and manage funds, safeguarded by bank-level encryption and fraud protection. Social savings funds provide collective security through pooled resources and community oversight, reducing individual risk by distributing savings across several members. Both options ensure access control and safety measures, but joint accounts offer more direct, regulated access, while social savings emphasize communal trust and mutual accountability.
Making the Right Choice for Collaborative Saving
Choosing between a joint savings account and a social savings fund depends on the level of shared control and purpose of the savings. Joint savings accounts offer direct, immediate access for all account holders to manage funds collaboratively, making them ideal for everyday expenses or family finance management. Social savings funds, often structured within community groups, emphasize collective responsibility and longer-term goals, providing benefits like pooled resources and increased financial discipline through group accountability.
Related Important Terms
Joint Account Automation
Joint savings accounts automate fund management by allowing multiple account holders to access and contribute to a single balance, streamlining deposit tracking and withdrawal processes. This automation enhances transparency and simplifies monitoring contributions compared to social savings funds, which often require manual coordination among participants.
Social Savings Pools
Social savings pools enable collective contribution and shared access to funds, fostering community-driven financial growth and risk mitigation. Unlike joint savings accounts that involve limited participants, social savings pools leverage group dynamics to enhance capital accumulation and provide broader social benefits.
Multi-Signature Withdrawal
A Joint Savings Account allows multiple account holders to manage funds with individual access, but typically requires only one signature for withdrawals, increasing the risk of unauthorized spending. In contrast, a Social Savings Fund uses multi-signature withdrawal protocols, requiring approval from multiple participants before funds can be accessed, enhancing security and collaborative financial control.
Collective Goal Tracking
Joint Savings Accounts allow multiple individuals to pool money with transparent, real-time tracking of contributions, enabling efficient collective goal achievement. Social Savings Funds leverage group commitments and peer accountability, enhancing motivation and disciplined saving toward shared financial objectives.
Peer-to-Peer Savings Circles
Peer-to-peer savings circles in joint savings accounts enable members to pool funds collaboratively, enhancing trust and accountability while providing flexible access to pooled resources. Social savings funds aggregate contributions from multiple participants, supporting collective goals and often incorporating structured withdrawal plans to optimize financial discipline and growth.
Shared Savings Ledger
A Shared Savings Ledger in Joint Savings Accounts enables transparent tracking of individual contributions and withdrawals, fostering collaborative financial management among account holders. In contrast, a Social Savings Fund leverages collective pooling of resources with community-governed transaction records, enhancing accountability and equitable distribution through a decentralized savings ledger system.
Micro-Group Fundraising
Joint savings accounts enable members to pool resources with shared access and decision-making, promoting transparency and accountability within micro-groups. Social savings funds, designed for collective micro-group fundraising, leverage communal trust to accumulate capital efficiently, often incorporating structured contribution schedules and targeted use of funds for group welfare or investment projects.
Digital Chit Fund
A Joint Savings Account allows multiple individuals to pool funds with shared access and control, offering straightforward tracking but limited structured returns compared to a Social Savings Fund. Digital Chit Funds, a type of Social Savings Fund, leverage technology to facilitate transparent, scheduled contributions and auctions, providing members with flexible credit access and potential higher returns through collective savings.
Friends & Family Savings Pods
Joint Savings Accounts allow friends and family to pool funds with easy access and shared control, promoting transparency and immediate liquidity. Social Savings Funds, structured as savings pods, leverage collective contributions and group trust to encourage disciplined saving habits and potentially higher interest returns through cooperative investments.
Social Smart Contracts
Social Savings Funds leveraging social smart contracts automate collective contributions and transparent fund management, enhancing trust and accountability among members. Unlike joint savings accounts, these decentralized mechanisms reduce reliance on traditional banks, enable programmable rules, and ensure secure, immutable records of transactions.
Joint Savings Account vs Social Savings Fund for savings. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com