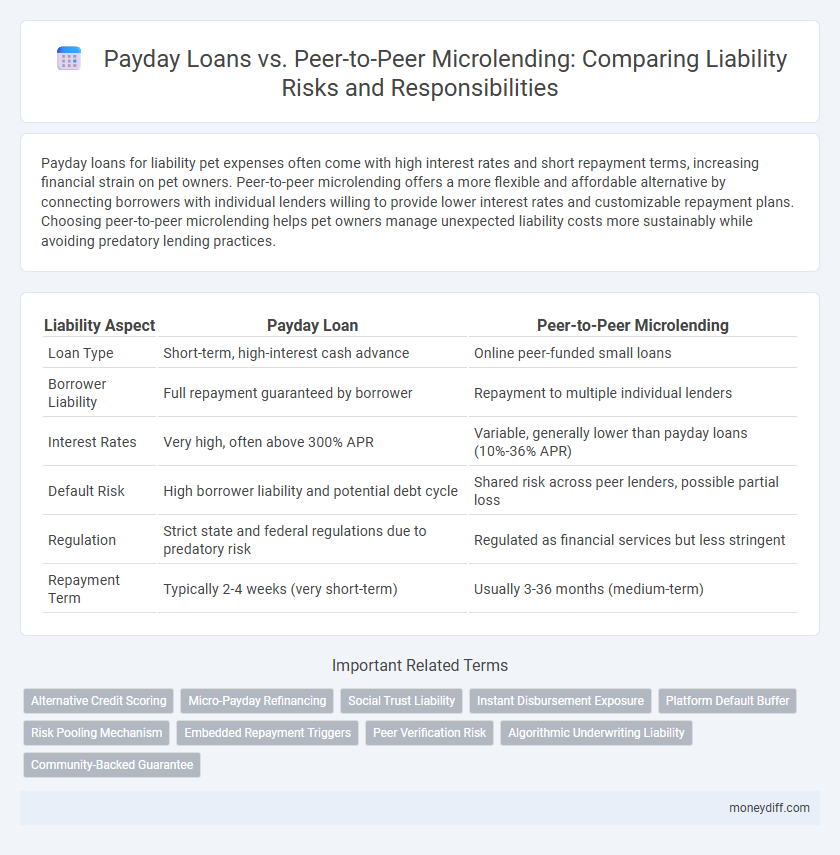
Payday loans for liability pet expenses often come with high interest rates and short repayment terms, increasing financial strain on pet owners. Peer-to-peer microlending offers a more flexible and affordable alternative by connecting borrowers with individual lenders willing to provide lower interest rates and customizable repayment plans. Choosing peer-to-peer microlending helps pet owners manage unexpected liability costs more sustainably while avoiding predatory lending practices.
Table of Comparison
| Liability Aspect | Payday Loan | Peer-to-Peer Microlending |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Type | Short-term, high-interest cash advance | Online peer-funded small loans |
| Borrower Liability | Full repayment guaranteed by borrower | Repayment to multiple individual lenders |
| Interest Rates | Very high, often above 300% APR | Variable, generally lower than payday loans (10%-36% APR) |
| Default Risk | High borrower liability and potential debt cycle | Shared risk across peer lenders, possible partial loss |
| Regulation | Strict state and federal regulations due to predatory risk | Regulated as financial services but less stringent |
| Repayment Term | Typically 2-4 weeks (very short-term) | Usually 3-36 months (medium-term) |
Understanding Liability in Payday Loans
Payday loans carry significant borrower liability due to high interest rates and fees, often resulting in automated withdrawals that can lead to overdrafts and increased debt cycles. Peer-to-peer microlending distributes liability among multiple individual lenders, reducing immediate financial risk but requiring clear repayment agreements to avoid default consequences. Understanding these differing liability structures is crucial for borrowers to manage risks effectively and maintain financial stability.
Peer-to-Peer Microlending: Assessing Borrower Obligations
Peer-to-peer microlending creates specific borrower obligations by formalizing liabilities through transparent contracts and often incorporating credit scoring systems to mitigate default risk. Unlike traditional payday loans, these platforms usually offer lower interest rates and structured repayment plans, reducing the likelihood of excessive borrower indebtedness. Legal frameworks governing peer-to-peer lending promote accountability and provide clearer recourse options in cases of borrower non-compliance or default.
Comparing Liability Structures: Payday Loans vs P2P Microlending
Payday loans carry a high liability risk due to their short-term, high-interest structure and borrower default rates, often resulting in significant financial burdens. Peer-to-peer microlending distributes risk among multiple individual lenders, reducing liability for each participant and allowing for diversified exposure. The P2P model generally offers more flexible repayment options, lowering default risks compared to rigid payday loan terms.
Default Risks and Consequences in Payday Lending
Payday loans carry a high default risk due to their short-term, high-interest structure, often leading borrowers into a cycle of debt and escalating liabilities. In contrast, peer-to-peer microlending typically offers lower interest rates and more flexible repayment terms, reducing the likelihood of default and severe financial consequences. Defaulting on payday loans often results in additional fees, legal actions, and damaged credit scores, significantly increasing a borrower's financial liability.
P2P Lender Exposure to Borrower Default
Peer-to-peer (P2P) microlending exposes lenders to higher risk of borrower default compared to payday loans due to lack of stringent credit checks and the informal nature of many P2P platforms. Unlike payday lenders that often secure repayment through upfront fees and short loan terms, P2P lenders face direct liability for unrecovered funds if borrowers fail to repay. This exposure necessitates robust risk assessment models and diversified lending portfolios to mitigate potential financial losses in P2P microlending.
Legal Implications of Loan Repayment Failure
Payday loans often carry strict legal repercussions for repayment failure, including high penalties, potential lawsuits, and damage to credit scores due to their regulated, short-term, high-interest nature. Peer-to-peer microlending presents a more flexible legal framework with fewer penalties and personalized repayment terms, reducing the risk of severe legal consequences and enabling negotiated resolutions between borrowers and individual lenders. Understanding these contrasting liability risks is crucial for borrowers to navigate repayment obligations and potential legal actions effectively.
Regulatory Protections for Borrowers and Lenders
Payday loans are subject to strict regulatory frameworks including caps on interest rates and mandatory disclosure requirements, aiming to protect borrowers from excessive debt and lenders from legal risks. Peer-to-peer microlending platforms operate under varying regulations depending on jurisdiction, often involving licensing and borrower-lender risk assessments to ensure transparency and reduce default risks. Regulatory protections in both models focus on safeguarding financial liability by promoting fair lending practices and enforcing dispute resolution mechanisms for all parties involved.
Credit Score Impact: Liability Considerations
Payday loans typically have a higher risk of negatively impacting credit scores due to their short-term nature and steep repayment terms, increasing borrowers' liability. Peer-to-peer microlending platforms often report payment activity to credit bureaus, potentially improving credit scores if repayments are timely, thereby reducing liability concerns. Evaluating the liability impact on credit scores is crucial when choosing between payday loans and peer-to-peer microlending.
Loan Agreement Transparency and Hidden Liabilities
Payday loans often feature opaque loan agreements with high interest rates and hidden fees that can significantly increase borrower liability. Peer-to-peer microlending platforms typically offer more transparent terms, clearly outlining interest rates and repayment schedules to reduce unexpected liabilities. Transparent loan agreements in microlending help borrowers better understand their obligations, minimizing the risk of unmanageable debt.
Strategies to Minimize Liability in Short-Term Borrowing
Payday loans often carry higher liability risks due to steep interest rates and aggressive repayment terms, making strategic liability management essential. Peer-to-peer microlending platforms provide more transparent terms and potentially lower interest rates, which can reduce borrower liability when properly assessed through credit evaluations. Incorporating clear contractual agreements and understanding regulatory protections further minimizes liability exposure in short-term borrowing scenarios.
Related Important Terms
Alternative Credit Scoring
Payday loans typically rely on traditional credit scores, resulting in higher liability risks due to limited borrower evaluation, whereas peer-to-peer microlending platforms utilize alternative credit scoring methods such as social data and transaction history, enhancing risk assessment accuracy and reducing default liability. Incorporating alternative credit scoring in peer-to-peer microlending promotes more inclusive lending and mitigates potential financial liabilities linked to borrower creditworthiness.
Micro-Payday Refinancing
Micro-payday refinancing in peer-to-peer microlending reduces liability risks compared to traditional payday loans by distributing repayment obligations among multiple individual lenders rather than a single predatory lender. This model enhances borrower affordability and lowers default rates, mitigating financial liability and fostering more responsible debt management.
Social Trust Liability
Payday loans often carry high social trust liability due to aggressive repayment terms and interest rates that can harm borrower relationships and community reputation. Peer-to-peer microlending reduces social trust liability by fostering transparent, trust-based connections between lenders and borrowers, promoting accountability and mutual respect.
Instant Disbursement Exposure
Payday loans carry higher liability risks due to instant disbursement exposure, increasing the lender's potential for default and regulatory scrutiny. Peer-to-peer microlending distributes this exposure across multiple investors, reducing individual liability while maintaining faster access to funds.
Platform Default Buffer
Payday loans typically lack a robust platform default buffer, increasing borrower liability risk as lenders face limited protection against defaults. In contrast, peer-to-peer microlending platforms often implement a default buffer fund that absorbs some losses, mitigating personal liability for lenders and enhancing overall financial security.
Risk Pooling Mechanism
Payday loans concentrate risk on individual borrowers, often leading to higher default rates and significant personal liability without risk-sharing benefits. Peer-to-peer microlending distributes liability across a diverse group of lenders through a risk pooling mechanism, reducing the financial impact on any single participant and enhancing overall credit risk management.
Embedded Repayment Triggers
Payday loans feature embedded repayment triggers tied to borrower's next paycheck, creating automatic debt obligations that increase liability risk. Peer-to-peer microlending typically uses flexible repayment schedules without rigid triggers, reducing sudden liability burdens for borrowers.
Peer Verification Risk
Peer-to-peer microlending presents a higher peer verification risk compared to payday loans, as lenders rely on less standardized borrower screening processes and social trust, potentially increasing the chance of default. In contrast, payday loan providers typically implement stringent credit checks and legal safeguards, minimizing liability exposure for lenders.
Algorithmic Underwriting Liability
Algorithmic underwriting in payday loans often involves higher liability risks due to automated decision-making processes that may overlook borrower-specific nuances, increasing default likelihood and regulatory scrutiny. In contrast, peer-to-peer microlending platforms incorporate more transparent and adaptive algorithms that distribute liability across multiple lenders, reducing individual risk exposure and enhancing compliance with lending regulations.
Community-Backed Guarantee
Peer-to-peer microlending offers a community-backed guarantee that mitigates individual liability by distributing risk among multiple lenders, whereas payday loans place full liability on the borrower with fixed, high-interest repayment terms. This community-backed model enhances accountability and reduces default risks, making peer-to-peer microlending a more reliable option for managing financial liabilities.
Payday Loan vs Peer-to-Peer Microlending for liability. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com