Dividend stocks offer consistent income through regular payouts, attracting investors seeking immediate cash flow. Dividend-growth investing emphasizes companies with increasing dividends over time, combining income with potential capital appreciation. This strategy often suits long-term investors aiming to build wealth through compounding returns and inflation protection.
Table of Comparison
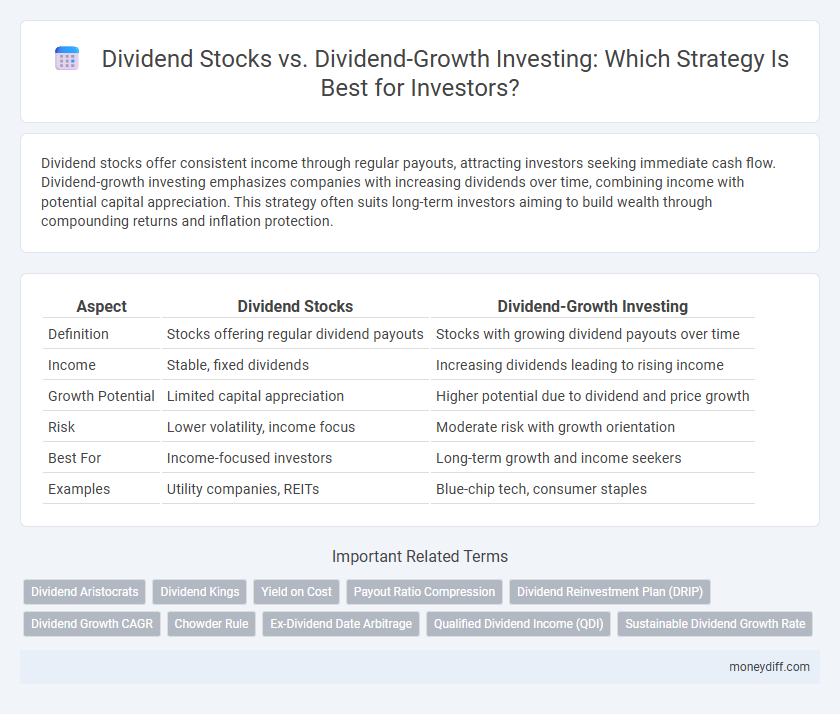
| Aspect | Dividend Stocks | Dividend-Growth Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stocks offering regular dividend payouts | Stocks with growing dividend payouts over time |
| Income | Stable, fixed dividends | Increasing dividends leading to rising income |
| Growth Potential | Limited capital appreciation | Higher potential due to dividend and price growth |
| Risk | Lower volatility, income focus | Moderate risk with growth orientation |
| Best For | Income-focused investors | Long-term growth and income seekers |
| Examples | Utility companies, REITs | Blue-chip tech, consumer staples |
Understanding Dividend Stocks: A Basic Overview
Dividend stocks are shares in companies that regularly distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders as dividends, providing a steady income stream. These stocks typically belong to established companies with stable cash flows and a history of consistent dividend payments, such as utilities or consumer staples. Investors seeking reliable income often prioritize dividend yield, while those focused on long-term wealth may consider dividend growth rates to benefit from rising payouts and compounded returns.
What is Dividend-Growth Investing?
Dividend-Growth Investing focuses on purchasing stocks of companies that consistently increase their dividend payouts over time, aiming for long-term capital appreciation and a steadily rising income stream. This strategy emphasizes the reinvestment of dividends to compound returns, benefiting from both dividend increases and potential stock price appreciation. Key metrics such as dividend growth rate, payout ratio, and earnings stability are critical for evaluating dividend-growth stocks.
Key Differences: Dividend Stocks vs Dividend-Growth Strategies
Dividend stocks provide regular income through consistent payouts, appealing to investors seeking immediate cash flow, while dividend-growth investing emphasizes increasing dividends over time for long-term wealth accumulation. Dividend-growth strategies often involve companies with strong earnings growth and sustainable payout ratios, promoting compounding returns. Key differences include income predictability in dividend stocks versus capital appreciation potential in dividend-growth approaches.
Risk and Reward: Evaluating Each Investment Approach
Dividend stocks offer immediate income streams with relatively lower risk due to established companies providing consistent payouts, while dividend-growth investing targets capital appreciation by reinvesting dividends into companies with increasing payout potential, which may carry higher volatility. Evaluating risk involves assessing market stability and company financial health, with dividend-growth investments potentially delivering higher long-term rewards through compounding and inflation protection. Balancing these approaches depends on an investor's risk tolerance and income needs, optimizing portfolio diversification and growth prospects.
Income Stability: Consistent vs Growing Payouts
Dividend stocks offer consistent income stability with regular, predictable payouts that appeal to investors seeking dependable cash flow. Dividend-growth investing focuses on companies with a history of increasing dividends over time, providing growing income that can help combat inflation and enhance purchasing power. Balancing these strategies allows investors to achieve both stable income and long-term income growth tailored to their financial goals.
Portfolio Diversification: Which Strategy Fits Best?
Dividend stocks provide steady income streams ideal for conservative portfolios seeking immediate cash flow, while dividend-growth investing emphasizes compounding returns through increasing payouts, suitable for long-term wealth accumulation. Incorporating both strategies enhances portfolio diversification by balancing current income with capital appreciation, reducing risk across varying market conditions. Assessing investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon determines which approach best aligns with an investor's diversification needs.
Tax Implications of Dividend Income
Dividend stocks often generate higher immediate income but may incur higher tax liabilities due to qualified and non-qualified dividend distinctions. Dividend-growth investing focuses on reinvesting dividends, potentially benefiting from long-term capital gains tax rates when shares are sold. Tax efficiency varies by account type, with tax-advantaged accounts mitigating ordinary dividend income taxes, making choice of investment strategy crucial for optimizing after-tax returns.
Historical Performance: Comparing Long-Term Returns
Dividend stocks have historically provided steady income with moderate capital appreciation, offering an average annual return of around 7-9% over the past few decades. Dividend-growth investing, focusing on companies with consistent dividend increases, has often outperformed static dividend stocks by delivering higher total returns near 10-12% annually due to reinvested dividends and compounding growth. Long-term data from markets like the S&P 500 reveal that dividend-growth stocks tend to exhibit stronger resilience during downturns and greater wealth accumulation over 20+ years.
Investor Profiles: Who Should Choose Which Strategy?
Dividend stocks suit investors seeking immediate income streams with relatively stable payouts, often appealing to retirees or those requiring consistent cash flow. Dividend-growth investing targets investors aiming for long-term capital appreciation combined with increasing dividend payments, ideal for younger investors with a longer time horizon. Risk tolerance and income needs critically influence whether an investor prefers the steady yield of dividend stocks or the compounding growth of dividend-growth strategies.
Building a Winning Investment Portfolio with Dividends
Dividend stocks provide consistent income through regular payouts, making them ideal for investors seeking steady cash flow in their portfolio. Dividend-growth investing focuses on companies with increasing dividend payouts, which can enhance long-term capital appreciation and help combat inflation. Combining both strategies creates a balanced portfolio that maximizes income stability while benefiting from potential growth and compounding returns.
Related Important Terms
Dividend Aristocrats
Dividend Aristocrats, a select group of S&P 500 companies with 25+ consecutive years of dividend increases, offer reliable income streams and resilience during market downturns, making them a preferred choice for dividend-growth investing; their consistent dividend growth often outpaces inflation, enhancing long-term returns. In contrast, traditional dividend stocks may provide higher immediate yields but lack the proven track record of increasing payouts, which can limit capital appreciation and income sustainability over time.
Dividend Kings
Dividend Kings represent a select group of companies with over 50 consecutive years of dividend increases, offering stable income and potential capital appreciation for dividend-growth investors. Comparing dividend stocks with high current yields to Dividend Kings highlights a trade-off between immediate income and long-term, inflation-resistant growth through sustained dividend increases.
Yield on Cost
Dividend stocks provide a steady income through current yield, while dividend-growth investing emphasizes increasing yield on cost over time by reinvesting dividends and benefiting from compounding growth. Focusing on yield on cost allows investors to track the effective return on their initial investment, highlighting the long-term value of dividend growth strategies compared to static dividend yields.
Payout Ratio Compression
Dividend stocks often feature higher initial yields but can experience payout ratio compression as earnings fluctuate, potentially limiting dividend sustainability. Dividend-growth investing targets companies with steadily increasing earnings, reducing the risk of payout ratio compression and supporting long-term income growth.
Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP)
Dividend stocks offer immediate income through regular payouts, while dividend-growth investing prioritizes companies with increasing dividends, enhancing long-term portfolio growth. Using a Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP) amplifies compounded returns by automatically reinvesting dividends to purchase additional shares, accelerating wealth accumulation.
Dividend Growth CAGR
Dividend-growth investing typically offers higher long-term compound annual growth rates (CAGR) by reinvesting steadily increasing dividends, which compounds wealth more effectively compared to traditional dividend stocks that provide static or lower dividend yields. Focusing on companies with consistent dividend growth rates of 6% or higher can significantly outperform fixed-yield dividend stocks in total returns over time.
Chowder Rule
The Chowder Rule guides investors to target dividend stocks with a yield plus growth rate exceeding 12%, helping balance immediate income and long-term capital appreciation. Dividend-growth investing focuses on companies with strong and consistent dividend increases, potentially leading to higher total returns over time despite lower initial yields.
Ex-Dividend Date Arbitrage
Dividend stocks provide immediate income through regular payouts, while dividend-growth investing emphasizes accumulating shares that increase dividends over time, enhancing long-term returns; the ex-dividend date arbitrage exploits price fluctuations around the ex-dividend date to capture short-term gains. Investors leveraging ex-dividend date arbitrage analyze the stock price drop typically equal to the dividend amount at the ex-dividend date, aiming to buy shares before this date and sell after to maximize profits from the dividend capture strategy.
Qualified Dividend Income (QDI)
Dividend stocks provide regular Qualified Dividend Income (QDI) that is taxed at favorable long-term capital gains rates, making them attractive for income-focused investors seeking tax efficiency. Dividend-growth investing emphasizes companies with increasing QDI payments over time, offering potential inflation protection and compounded wealth accumulation.
Sustainable Dividend Growth Rate
Dividend stocks provide immediate income through consistent payouts, whereas dividend-growth investing emphasizes sustainable dividend growth rate to build long-term wealth by reinvesting increasing dividends. Focusing on companies with a high and stable sustainable dividend growth rate ensures better inflation protection and compounding returns over time.
Dividend Stocks vs Dividend-Growth Investing for Investment. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com