Active income requires direct effort and time, such as salaries, freelance work, or consulting fees, providing immediate and consistent cash flow. Passive income generates earnings with minimal daily involvement, stemming from investments, rental properties, or online businesses, offering long-term financial stability. Balancing both income types enhances financial security by combining steady paychecks with growth potential.
Table of Comparison
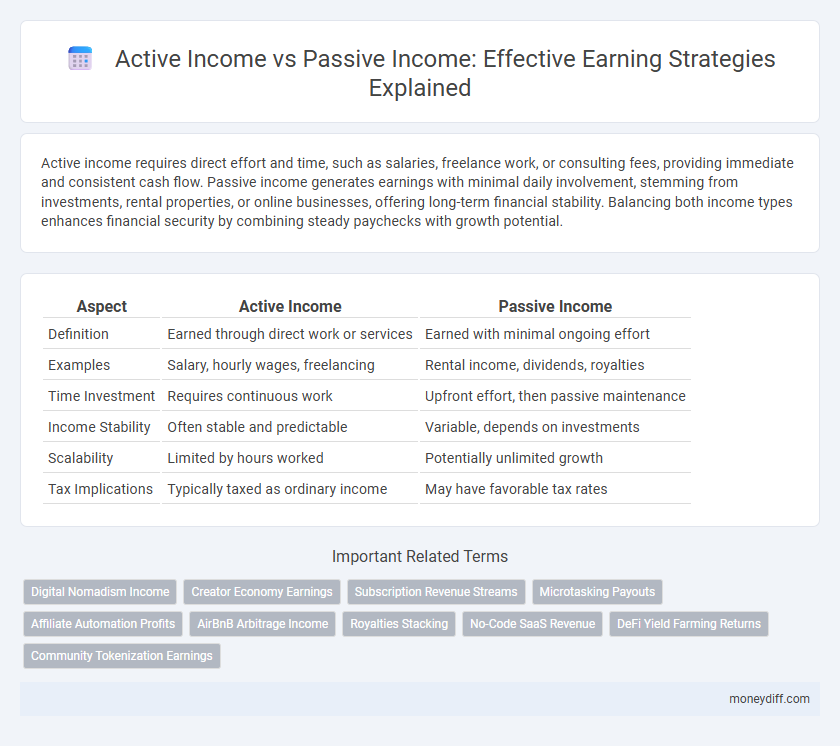
| Aspect | Active Income | Passive Income |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Earned through direct work or services | Earned with minimal ongoing effort |
| Examples | Salary, hourly wages, freelancing | Rental income, dividends, royalties |
| Time Investment | Requires continuous work | Upfront effort, then passive maintenance |
| Income Stability | Often stable and predictable | Variable, depends on investments |
| Scalability | Limited by hours worked | Potentially unlimited growth |
| Tax Implications | Typically taxed as ordinary income | May have favorable tax rates |
Understanding Active vs Passive Income
Active income requires continuous effort and time, typically generated through wages, salaries, or freelance work, directly tied to the amount of work performed. Passive income comes from investments, rental properties, or business ventures where ongoing effort is minimal after initial setup, allowing earnings to accumulate independently. Understanding the distinction helps individuals balance immediate cash flow needs with long-term wealth building strategies.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Income
Active income requires continuous effort and time, such as salaries, wages, or freelance work, directly tied to hours worked. Passive income generates revenue with minimal ongoing effort, including rental properties, dividends, and royalties, allowing earnings to accumulate even when not actively working. The key difference lies in the dependency on active involvement, where active income stops when work ceases, while passive income often provides ongoing financial benefits.
Advantages of Active Income Streams
Active income streams provide immediate and consistent cash flow through direct labor or services rendered, ensuring financial stability and control over earnings. This type of income allows individuals to leverage their skills and time efficiently, often resulting in higher hourly rates compared to passive income sources. Active income can also offer benefits such as employer-sponsored healthcare, retirement plans, and opportunities for career advancement.
Benefits of Passive Income Sources
Passive income sources offer the significant benefit of generating earnings without continuous active effort, allowing individuals to build wealth steadily over time. Examples such as rental properties, dividend stocks, and online businesses create financial stability and diversification while freeing up time for personal pursuits or additional investments. This income model enhances long-term financial security by reducing dependence on a single job or employer.
Common Examples of Active Income
Active income typically includes wages, salaries, tips, and commissions earned through direct work or services provided. Common examples are hourly jobs, freelancing, and consulting, where income depends on time and effort invested. This type of income is often subject to payroll taxes and stops when work ceases, unlike passive income streams.
Popular Passive Income Opportunities
Popular passive income opportunities include real estate rentals, dividend-paying stocks, and creating digital products such as e-books or online courses. These methods generate consistent revenue with minimal daily effort, allowing individuals to diversify their income streams beyond traditional active employment. Leveraging automated systems and investments can maximize earnings while reducing time commitment compared to active income strategies.
Balancing Active and Passive Earnings
Balancing active income, derived from direct work such as salaries or freelancing, with passive income from investments like dividends, rental properties, or royalties creates a diversified earning strategy. Effective income management involves allocating time and resources to maintain active income streams while building and sustaining passive income to ensure financial stability and growth. Optimizing this balance maximizes cash flow, reduces risk, and builds long-term wealth.
Tax Implications: Active vs Passive Income
Active income, generated through direct labor such as wages or business profits, is typically taxed at higher ordinary income tax rates and subject to payroll taxes like Social Security and Medicare. Passive income, derived from investments such as rental properties or dividends, often benefits from lower tax rates, including capital gains tax advantages and possible deductions for expenses. Understanding these tax implications helps optimize earnings strategies by balancing immediate income needs with long-term tax efficiency.
Building Sustainable Income: Strategies and Tips
Building sustainable income involves balancing active income, generated through direct labor and services, with passive income streams that require minimal ongoing effort, such as investments, rental properties, or royalties. Diversifying income sources reduces financial risk and creates long-term wealth, with emphasis on reinvesting profits and automating passive revenue channels for scalability. Strategic planning includes leveraging skills for high-value active income and allocating resources to passive opportunities that compound returns over time.
Choosing the Right Earning Strategy for Your Goals
Active income requires continuous effort through work or services, offering immediate cash flow but limited scalability. Passive income generates earnings from investments or automated systems, enabling long-term growth with minimal daily involvement. Selecting the right strategy depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and desired time commitment for maximizing income potential.
Related Important Terms
Digital Nomadism Income
Active income for digital nomads typically involves work such as freelance writing, programming, or consulting, earning money through direct labor and real-time engagement, while passive income streams include affiliate marketing, digital product sales, or automated online courses that generate revenue with minimal ongoing effort. Balancing these income types enhances financial stability and flexibility, critical for sustaining a location-independent lifestyle.
Creator Economy Earnings
Active income in the creator economy is generated through direct engagement like content creation, streaming, or freelance services, requiring continuous effort and time investment. Passive income arises from monetized digital assets such as ad revenue, royalties, or subscription models, providing creators scalable earnings with less ongoing input.
Subscription Revenue Streams
Subscription revenue streams generate consistent passive income by charging customers a recurring fee, allowing businesses to scale earnings without continuous active involvement. Unlike active income, which requires ongoing work and time investment, subscription models optimize cash flow stability and long-term growth potential.
Microtasking Payouts
Active income from microtasking payouts requires continuous effort and timely task completion, generating immediate earnings based on activities performed. Passive income strategies rely on scalable digital assets or investments that yield returns without constant input, contrasting with microtasking's direct, effort-dependent revenue streams.
Affiliate Automation Profits
Active income requires direct involvement and continuous effort, while passive income generates earnings with minimal ongoing work; affiliate automation profits exemplify a passive income strategy by leveraging automated systems to consistently drive sales and commissions without daily hands-on management. Implementing affiliate automation tools can optimize revenue streams by scaling outreach and maximizing conversions, offering sustainable income growth beyond traditional active labor.
AirBnB Arbitrage Income
Airbnb arbitrage income leverages active management skills by renting properties long-term and subleasing them short-term for higher returns, blending aspects of active income through hands-on operations with passive income from property rentals. This strategy maximizes cash flow by optimizing occupancy rates and nightly pricing without owning the real estate, offering a scalable approach to income generation.
Royalties Stacking
Royalties stacking leverages multiple income streams from intellectual property to create a scalable active income source that gradually transitions into passive revenue generation. By strategically acquiring and managing diverse royalties, individuals enhance long-term financial stability and compound earnings with minimal ongoing effort.
No-Code SaaS Revenue
Active income from No-Code SaaS requires continuous user engagement and management, generating revenue through subscription fees or service usage. Passive income stems from automated No-Code SaaS platforms that scale with minimal intervention, leveraging recurring payments and low maintenance for sustained earnings.
DeFi Yield Farming Returns
DeFi yield farming returns provide an innovative form of passive income by allowing users to earn rewards through liquidity provision without active daily management. Compared to active income, which requires continuous effort and time investment, DeFi yield farming leverages decentralized finance protocols to generate automated, compounding returns on crypto assets.
Community Tokenization Earnings
Community tokenization earnings leverage blockchain technology to transform traditional active income into scalable passive income streams by enabling fractional ownership and profit-sharing within decentralized communities. This strategy empowers participants to earn continuously from digital assets and community-driven projects without direct, ongoing labor.
Active Income vs Passive Income for earning strategies. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com