Bank credit offers borrowers structured loan terms, regulated interest rates, and established credit checks, providing a reliable and secure borrowing experience. Peer-to-peer credit connects borrowers directly with individual lenders, often resulting in more flexible loan options and potentially lower rates but with varying risk levels and less regulatory oversight. Choosing between these options depends on the borrower's priority for security, speed, and personalized terms versus standardized processes and institutional guarantees.
Table of Comparison
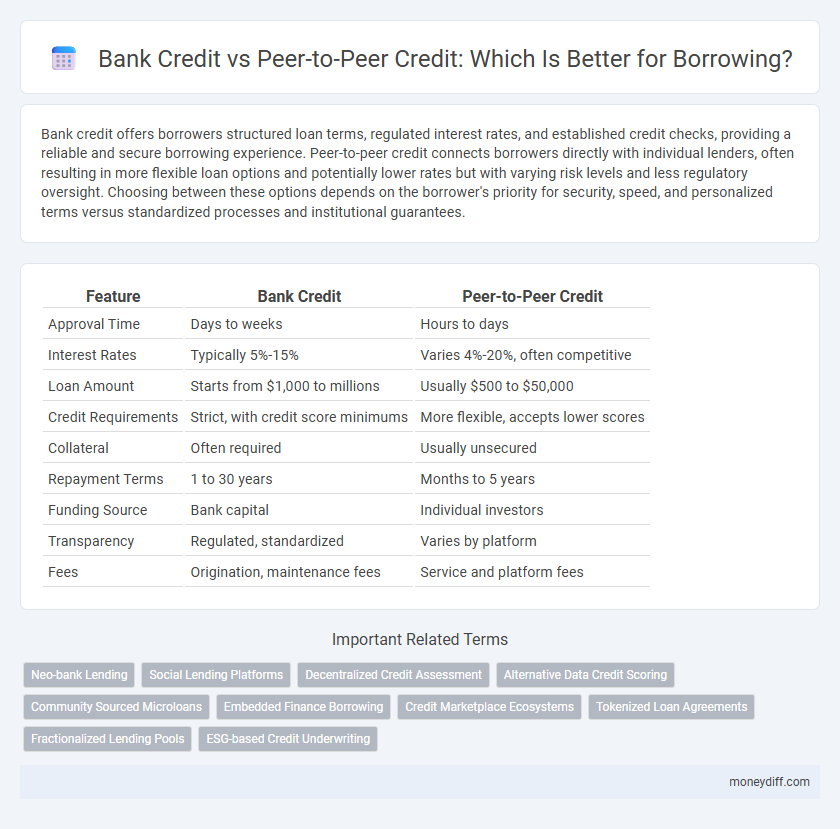
| Feature | Bank Credit | Peer-to-Peer Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Approval Time | Days to weeks | Hours to days |
| Interest Rates | Typically 5%-15% | Varies 4%-20%, often competitive |
| Loan Amount | Starts from $1,000 to millions | Usually $500 to $50,000 |
| Credit Requirements | Strict, with credit score minimums | More flexible, accepts lower scores |
| Collateral | Often required | Usually unsecured |
| Repayment Terms | 1 to 30 years | Months to 5 years |
| Funding Source | Bank capital | Individual investors |
| Transparency | Regulated, standardized | Varies by platform |
| Fees | Origination, maintenance fees | Service and platform fees |
Introduction to Bank Credit and Peer-to-Peer Credit
Bank credit involves borrowing funds directly from financial institutions that use established credit scoring systems and regulatory frameworks to assess borrower risk and offer various loan products. Peer-to-peer credit connects individual borrowers with private lenders through online platforms, leveraging alternative data and social trust mechanisms to potentially provide faster, more flexible credit options. Both models impact credit access by balancing risk evaluation, interest rates, and borrower requirements within distinct financial ecosystems.
How Bank Credit Works
Bank credit operates through a financial institution that evaluates the borrower's creditworthiness using credit scores, income verification, and repayment history before approving loans. Interest rates and repayment terms are fixed or variable, often influenced by central bank policies, ensuring regulatory compliance and risk management. Unlike peer-to-peer credit, bank credit provides structured lending with stronger consumer protections and access to larger loan amounts.
Understanding Peer-to-Peer Credit Platforms
Peer-to-peer credit platforms connect borrowers directly with individual lenders through online marketplaces, bypassing traditional bank intermediaries and often offering lower interest rates and faster approval processes. These platforms use algorithms to assess creditworthiness based on alternative data, expanding access to credit for individuals with non-traditional credit histories. Risks include less regulatory oversight and potential variability in lender reliability compared to conventional bank credit services.
Eligibility Criteria: Bank Credit vs Peer-to-Peer Credit
Bank credit typically requires a strong credit score, proof of stable income, and extensive documentation, making eligibility more stringent. Peer-to-peer credit platforms often have more flexible criteria, focusing on alternative data such as social reputation and digital transaction history. This flexibility allows borrowers with limited traditional credit history to access loans more easily.
Interest Rates Comparison: Banks vs P2P Lending
Bank credit typically offers lower interest rates due to established regulatory frameworks and economies of scale, making it cost-effective for borrowers with strong credit profiles. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms often present higher interest rates reflecting increased risk and less stringent underwriting, though they provide flexible terms and quicker access to funds. Comparing interest rates, bank loans usually range from 5% to 12%, whereas P2P loans vary widely between 7% and 24%, depending on borrower creditworthiness and market conditions.
Speed and Accessibility of Credit Options
Bank credit typically involves longer processing times due to strict verification processes and regulatory compliance, which can delay loan approval and disbursement. Peer-to-peer (P2P) credit platforms offer faster access to funds by leveraging online technology and streamlined approval systems, often providing loans within days. Accessibility is enhanced in P2P lending through reduced eligibility criteria and the ability to reach underserved borrowers who may not qualify for traditional bank loans.
Security and Regulatory Differences
Bank credit offers higher regulatory oversight through established financial authorities such as the FDIC and Federal Reserve, ensuring depositor protection and strict lending standards. Peer-to-peer credit operates with less regulatory scrutiny, increasing risk exposure due to limited consumer protections and potential platform instability. Security in bank credit is reinforced by insured deposits and centralized governance, while P2P lending relies on decentralized platforms with variable risk management protocols.
Impact on Credit Score: Bank Loans vs P2P Loans
Bank credit typically reports to major credit bureaus, positively influencing credit scores when payments are made on time, whereas peer-to-peer (P2P) credit platforms may have inconsistent reporting practices that can limit their impact on credit score improvement. On-time repayments of bank loans contribute to a stronger credit history and higher credit scores due to regular reporting and the generational favoring of traditional credit models. P2P loans might offer easier access to funds, but the lack of consistent credit reporting often results in minimal credit score impact, making them less effective for borrowers aiming to build or improve credit.
Risks and Benefits of Each Borrowing Method
Bank credit offers stable interest rates and regulatory protection, minimizing default risk but often requires stringent eligibility criteria and longer approval times. Peer-to-peer credit provides faster access and potentially lower rates by connecting borrowers directly with individual lenders, though it carries higher risks due to less regulation and variable credit evaluation standards. Borrowers must weigh the security and predictability of bank credit against the flexibility and accessibility of peer-to-peer lending platforms.
Choosing the Right Credit Option for Your Financial Needs
Bank credit offers structured loan options with regulated interest rates, credit limits, and established credit evaluation criteria, providing reliability and protection under financial laws. Peer-to-peer credit connects borrowers directly with individual lenders through online platforms, often resulting in faster approval and potentially lower rates but with variable terms and less regulatory oversight. Assess your credit score, loan amount, repayment flexibility, and urgency to determine whether the traditional security of bank credit or the innovative convenience of P2P lending best aligns with your financial needs.
Related Important Terms
Neo-bank Lending
Neo-bank lending offers a streamlined, digital-first alternative to traditional bank credit by leveraging advanced algorithms for faster loan approvals and personalized interest rates. Peer-to-peer credit provides borrowers with access to community-driven funding, often featuring flexible terms, but neo-bank platforms combine the credibility of bank credit with enhanced user experience and automated risk assessment.
Social Lending Platforms
Bank credit typically involves traditional financial institutions offering loans with strict eligibility criteria, while peer-to-peer credit through social lending platforms connects borrowers directly with individual lenders, often providing more flexible terms and competitive interest rates. Social lending platforms leverage data-driven risk assessments and transparent peer reviews to facilitate credit access for underserved borrowers.
Decentralized Credit Assessment
Decentralized credit assessment in peer-to-peer credit platforms leverages blockchain technology and community-driven verification to evaluate borrower creditworthiness, reducing reliance on traditional credit bureaus used by banks. This innovative approach enhances transparency, lowers borrowing costs, and increases accessibility for underserved borrowers compared to conventional bank credit systems.
Alternative Data Credit Scoring
Bank credit typically relies on traditional credit scores derived from credit bureaus, while peer-to-peer credit platforms increasingly utilize alternative data credit scoring, incorporating factors such as social media activity, payment histories on utilities, and digital footprints. This alternative data approach enhances credit accessibility for borrowers with limited credit history, improving risk assessment accuracy and broadening lending opportunities.
Community Sourced Microloans
Community sourced microloans through peer-to-peer credit platforms offer borrowers access to flexible funding with potentially lower interest rates and faster approval compared to traditional bank credit. These decentralized lending networks leverage social trust and digital platforms to connect individual lenders directly with borrowers, enhancing financial inclusion and supporting micro-entrepreneurship.
Embedded Finance Borrowing
Embedded finance borrowing integrates bank credit seamlessly into digital platforms, offering borrowers access to traditional bank loans with enhanced convenience and security. Peer-to-peer credit within embedded finance leverages direct lender-borrower connections via technology, often providing faster approval and more flexible terms but with varied risk profiles compared to bank credit.
Credit Marketplace Ecosystems
Bank credit typically involves centralized institutions offering regulated loans with fixed interest rates and structured repayment terms, ensuring borrower security through credit scoring and collateral requirements. Peer-to-peer credit operates within decentralized credit marketplace ecosystems, connecting individual lenders and borrowers directly, often enabling competitive rates and flexible terms driven by real-time market dynamics and credit transparency.
Tokenized Loan Agreements
Bank credit typically involves traditional institutions offering loans secured by standardized contracts, while peer-to-peer credit leverages blockchain technology to enable tokenized loan agreements that enhance transparency, reduce intermediaries, and increase accessibility. Tokenized loan agreements digitize debt instruments on distributed ledgers, providing immutable records that facilitate faster settlement and customizable terms tailored to borrower and lender preferences.
Fractionalized Lending Pools
Bank credit offers traditional, centralized lending with strict eligibility and fixed interest rates, while peer-to-peer credit utilizes fractionalized lending pools allowing multiple investors to share risk and provide flexible loan terms. Fractionalized lending pools enhance liquidity and diversify credit sources, making peer-to-peer platforms more adaptable and accessible for borrowers with varied credit profiles.
ESG-based Credit Underwriting
Bank credit underwriting typically incorporates traditional financial metrics with emerging ESG criteria to assess borrower sustainability and risk, leveraging extensive data and regulatory frameworks. Peer-to-peer credit platforms increasingly integrate ESG-based underwriting models, using alternative data and community-driven evaluations to provide more inclusive and transparency-focused lending options.
Bank Credit vs Peer-to-Peer Credit for borrowing. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com