Bank statements provide a historical snapshot of transactions, offering detailed records that help track past spending and income patterns. Open banking data feeds deliver real-time access to financial information, enabling more proactive and automated money management through instant updates and insights. Combining both sources enhances cash flow analysis by blending accuracy with immediacy for better financial decision-making.
Table of Comparison
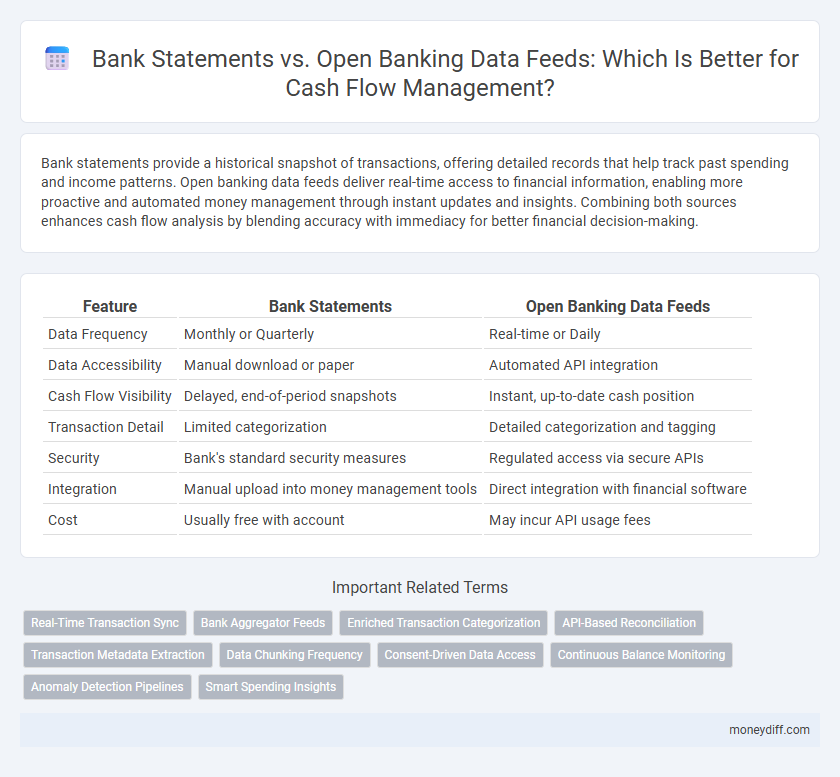
| Feature | Bank Statements | Open Banking Data Feeds |
|---|---|---|
| Data Frequency | Monthly or Quarterly | Real-time or Daily |
| Data Accessibility | Manual download or paper | Automated API integration |
| Cash Flow Visibility | Delayed, end-of-period snapshots | Instant, up-to-date cash position |
| Transaction Detail | Limited categorization | Detailed categorization and tagging |
| Security | Bank's standard security measures | Regulated access via secure APIs |
| Integration | Manual upload into money management tools | Direct integration with financial software |
| Cost | Usually free with account | May incur API usage fees |
Understanding Bank Statements in Cash Flow Management
Bank statements provide a historical record of all transactions within a specific period, essential for accurate cash flow tracking and reconciliation. By analyzing these statements, businesses can identify spending patterns, monitor account balances, and forecast future cash flow needs. However, their static nature limits real-time insights compared to open banking data feeds, which continuously update financial data for proactive money management.
What Are Open Banking Data Feeds?
Open banking data feeds enable direct, real-time streaming of transactional data from financial institutions to authorized third-party applications, enhancing cash flow visibility and money management accuracy. Unlike traditional bank statements that provide static, periodic snapshots, open banking feeds offer continuous updates, facilitating timely insights into income, expenses, and liquidity. These dynamic data streams empower businesses and individuals to make informed cash flow decisions based on the most current financial information available.
Accuracy: Bank Statements vs Open Banking Data
Bank statements provide historical, verified records of all transactions, ensuring high accuracy but with delayed updates often limited to monthly cycles. Open banking data feeds deliver real-time transaction information, offering up-to-date insights but potential minor inaccuracies due to ongoing data processing or categorization errors. For optimal money management, combining the precision of bank statements with the immediacy of open banking data enhances cash flow monitoring and decision-making.
Real-Time Access: The Open Banking Advantage
Open banking data feeds provide real-time access to financial information, enabling instant updates on transactions and balances compared to the delayed reporting often found in traditional bank statements. This immediate visibility enhances cash flow management by allowing businesses and individuals to make timely decisions based on accurate, up-to-the-minute data. Real-time data integration through open banking accelerates financial forecasting and improves liquidity monitoring for optimized money management.
Security Considerations: Traditional vs Open Banking
Bank statements offer a familiar security model based on encrypted document delivery and limited access permissions but can be vulnerable to delays and data manipulation. Open banking data feeds leverage OAuth standards and tokenized API access, enhancing real-time security and reducing fraud risk through granular consent management. Security protocols in open banking support continuous monitoring and immediate revocation of access, contrasting with the more static and manual control present in traditional bank statement processing.
Data Granularity and Categorization Comparison
Bank statements provide transaction summaries with limited categorization, often grouping expenses into broad categories such as "debits" and "credits," which restricts detailed cash flow analysis. Open banking data feeds offer higher data granularity by delivering real-time, itemized transaction information with enhanced categorization using AI-driven tagging, enabling more precise budgeting and personalized financial insights. The improved data segmentation in open banking facilitates deeper understanding of spending patterns, helping users optimize money management strategies more effectively than traditional bank statements.
Integration With Money Management Tools
Bank statements provide historical financial data in static formats, limiting real-time integration with money management tools. Open banking data feeds enable seamless, real-time access to transactional data through APIs, enhancing cash flow tracking and budgeting accuracy. Integration with open banking accelerates automated categorization, cash flow forecasting, and personalized financial insights for users.
User Experience: Manual Downloads vs Automated Feeds
Bank statements require users to manually download and upload files, causing delays and potential errors in cash flow tracking. Open banking data feeds provide real-time, automated access to transaction data, enhancing accuracy and immediacy in money management. This seamless integration improves user experience by reducing hassle and enabling timely financial decisions.
Costs and Accessibility of Data Sources
Bank statements often involve fees for paper copies or account access, while open banking data feeds generally provide real-time, cost-effective access to transaction information via APIs. Open banking enhances data accessibility by enabling seamless integration with money management apps and services, reducing manual entry and delays. Traditional bank statements may limit data granularity and frequency, whereas open banking data feeds offer continuous updates, improving cash flow monitoring and forecasting.
Choosing the Best Data Source for Effective Cash Flow Management
Bank statements provide historical transaction records essential for tracking past cash flow, while open banking data feeds offer real-time updates and richer insights into account activity. Utilizing open banking enables more dynamic cash flow management through instantaneous access to inflows and outflows, improving forecasting accuracy and liquidity planning. Integrating both sources can optimize financial decision-making by combining detailed historical data with current transactional context.
Related Important Terms
Real-Time Transaction Sync
Open banking data feeds provide real-time transaction synchronization, allowing users to monitor cash flow instantly, unlike traditional bank statements that update periodically. This immediate access to transaction data enhances money management by enabling timely budgeting decisions and fraud detection.
Bank Aggregator Feeds
Bank aggregator feeds provide real-time, consolidated access to multiple bank statements, enhancing cash flow visibility and accuracy for effective money management. This seamless integration of open banking data feeds reduces manual reconciliation and improves forecasting by leveraging up-to-date transaction insights across various accounts.
Enriched Transaction Categorization
Bank statements provide static records of transactions, whereas open banking data feeds offer enriched transaction categorization by delivering real-time, detailed insights into spending patterns and cash flow dynamics. Enhanced categorization through open banking enables more accurate budget forecasting and personalized money management strategies, improving financial decision-making efficiency.
API-Based Reconciliation
API-based reconciliation using open banking data feeds provides real-time, granular transaction details directly from financial institutions, enhancing cash flow visibility and accuracy compared to traditional bank statements that often suffer from delayed updates and limited data scope. This seamless integration enables automated matching of payments and receipts, reducing manual effort and improving liquidity forecasting in money management processes.
Transaction Metadata Extraction
Bank statements provide static records with limited transaction details, while open banking data feeds enable real-time access to enriched transaction metadata such as merchant category, transaction location, and spending patterns. Enhanced metadata extraction through open banking facilitates advanced cash flow analysis, automated categorization, and personalized financial insights for superior money management.
Data Chunking Frequency
Bank statements provide monthly snapshots of financial activity, limiting real-time cash flow insights, while open banking data feeds deliver granular, continuous transaction updates with higher data chunking frequency, enabling dynamic, up-to-date money management. Enhanced data chunking in open banking APIs supports precise cash flow forecasting and timely financial decision-making by capturing transactions as they occur.
Consent-Driven Data Access
Bank statements provide historical financial data through periodic snapshots, while open banking data feeds offer real-time access to transactional information driven by explicit user consent for seamless money management. Consent-driven data access ensures enhanced security and privacy by allowing users to control which financial data is shared and how it's utilized in cash flow analysis.
Continuous Balance Monitoring
Continuous balance monitoring leverages open banking data feeds to provide real-time, accurate insights into cash flow, surpassing traditional bank statements that offer only periodic snapshots. This dynamic data integration enables proactive financial decisions and improved liquidity management for businesses and individuals.
Anomaly Detection Pipelines
Bank statements provide historical snapshots of transactions, while open banking data feeds offer real-time access to financial activity, enabling more dynamic anomaly detection pipelines. Real-time data streams from open banking APIs enhance the accuracy and speed of identifying irregular cash flow patterns compared to periodic bank statement analysis.
Smart Spending Insights
Bank statements provide a historical record of transactions, while open banking data feeds enable real-time access to financial data, enhancing Smart Spending Insights by delivering up-to-date, personalized spending patterns and cash flow forecasts. Utilizing open banking data allows for dynamic budgeting and proactive money management, improving decision-making accuracy compared to traditional statement analysis.
Bank statements vs open banking data feeds for money management. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com