ETFs offer broad market exposure and low-cost access to a diversified portfolio, making them suitable for passive asset management strategies. Smart Beta focuses on systematic factor-based investing, aiming to enhance returns or reduce risk by weighting assets differently than traditional market-cap methods. Choosing between ETF and Smart Beta depends on whether the investor prefers simplicity and cost efficiency or targeted factor exposure to optimize asset allocation.
Table of Comparison
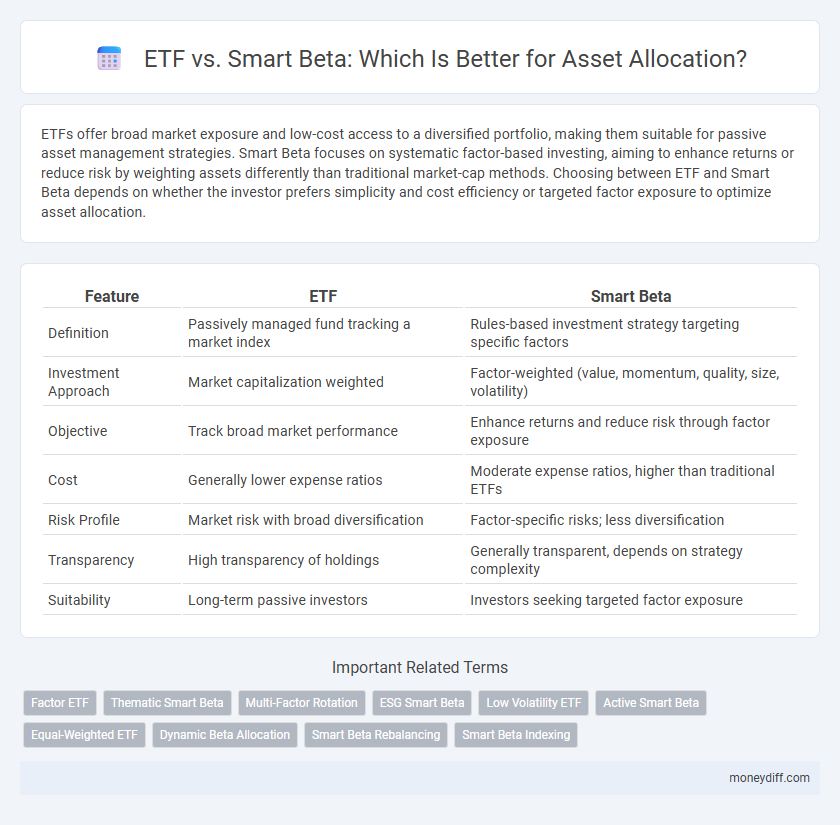
| Feature | ETF | Smart Beta |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Passively managed fund tracking a market index | Rules-based investment strategy targeting specific factors |
| Investment Approach | Market capitalization weighted | Factor-weighted (value, momentum, quality, size, volatility) |
| Objective | Track broad market performance | Enhance returns and reduce risk through factor exposure |
| Cost | Generally lower expense ratios | Moderate expense ratios, higher than traditional ETFs |
| Risk Profile | Market risk with broad diversification | Factor-specific risks; less diversification |
| Transparency | High transparency of holdings | Generally transparent, depends on strategy complexity |
| Suitability | Long-term passive investors | Investors seeking targeted factor exposure |
Understanding ETFs and Smart Beta: An Overview
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) provide investors with diversified exposure to various asset classes through a passive, market-cap weighted approach, enabling cost-effective portfolio management. Smart Beta strategies enhance traditional ETF frameworks by incorporating alternative weighting methods based on factors like value, momentum, or volatility to improve risk-adjusted returns. Understanding the structural differences between ETFs and Smart Beta products is crucial for optimizing asset allocation and aligning investment objectives with targeted performance outcomes.
Key Differences Between Traditional ETFs and Smart Beta
Traditional ETFs track market-cap-weighted indexes offering broad market exposure with low fees and high liquidity. Smart Beta ETFs utilize alternative weighting strategies based on factors like value, momentum, or volatility, aiming to enhance returns or reduce risk. These strategic weights provide targeted asset allocation, potentially outperforming traditional market-cap benchmarks over time.
How ETFs Work in Asset Management
ETFs function as pooled investment vehicles that trade on stock exchanges, allowing investors to buy shares representing a diversified portfolio of assets. By tracking an index or specific asset class, ETFs offer liquidity, transparency, and low expense ratios, making them efficient tools for asset allocation and risk management. Smart Beta ETFs blend traditional passive strategies with factor-based selection, aiming to enhance returns or reduce risk through systematic exposure to factors like value, momentum, or volatility.
The Principles Behind Smart Beta Strategies
Smart Beta strategies blend traditional indexing with active management by systematically selecting and weighting assets based on factors like value, momentum, and volatility, departing from market-cap weighting used in ETFs. These principles aim to enhance returns, reduce risk, or improve diversification through rules-based approaches that target specific investment factors. Comparing Smart Beta to conventional ETFs highlights the trade-off between capturing market returns and seeking factor-driven outperformance.
Performance Comparison: ETF vs. Smart Beta
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) provide broad market exposure with typically lower fees, while Smart Beta strategies aim to enhance returns or reduce risk by selecting and weighting assets based on specific factors such as value, momentum, or volatility. Performance comparison reveals that Smart Beta ETFs often outperform traditional ETFs in certain market conditions by exploiting persistent factor premiums, though they may also exhibit higher volatility and tracking error. Investors should evaluate historical returns, risk-adjusted metrics like Sharpe ratio, and expense ratios to determine which investment aligns best with their portfolio objectives.
Risk Factors: Assessing Volatility and Drawdowns
ETFs provide diversified exposure with generally lower volatility, but may still be affected by broad market risks and sector concentration. Smart Beta strategies target specific risk factors like value, momentum, or size, aiming to enhance returns while managing drawdowns through systematic rules. Evaluating historical volatility and maximum drawdown metrics is critical for comparing these asset approaches and aligning with investor risk tolerance.
Cost Efficiency: Fees and Expenses Compared
ETFs typically offer lower expense ratios compared to smart beta funds, enhancing cost efficiency for investors. Smart beta strategies often incur higher fees due to active management and complex portfolio construction. Investors seeking minimal cost exposure generally prefer ETFs to maximize net returns.
Diversification Benefits: ETF vs. Smart Beta Portfolios
ETF portfolios offer broad market exposure with diversified holdings across multiple sectors and asset classes, reducing idiosyncratic risk. Smart Beta strategies target specific factors such as value, momentum, or low volatility, enhancing diversification by blending systematic factor tilts with traditional asset exposure. Combining Smart Beta with ETFs can optimize diversification by balancing market replication and factor-driven returns, improving risk-adjusted performance.
Suitability for Different Investment Goals
ETFs offer broad market exposure with low costs, making them suitable for passive investors seeking diversification and long-term growth. Smart Beta strategies combine factor-based investing with ETF convenience, appealing to investors aiming for enhanced risk-adjusted returns or targeted exposure to factors like value, momentum, or quality. Choosing between ETFs and Smart Beta depends on goals: broad market participation favors traditional ETFs, while specific factor tilts or risk profiles align better with Smart Beta options.
Choosing Between ETFs and Smart Beta for Your Asset Strategy
ETFs offer broad market exposure with low-cost, passive management, ideal for investors seeking simplicity and liquidity. Smart Beta strategies combine rules-based factor investing with ETF structures to target specific risk premia such as value, momentum, or low volatility, aiming for enhanced returns or risk-adjusted performance. Selecting between ETFs and Smart Beta depends on your asset allocation goals, risk tolerance, and desire for tailored factor exposure within a diversified portfolio.
Related Important Terms
Factor ETF
Factor ETFs leverage specific investment factors such as value, momentum, or quality to optimize asset allocation, aiming to enhance returns and manage risk compared to traditional market-cap weighted ETFs. These smart beta strategies systematically capture factor premiums, providing a transparent and cost-efficient approach to asset management within the ETF structure.
Thematic Smart Beta
Thematic Smart Beta ETFs combine rule-based index strategies with thematic investing, targeting specific trends such as clean energy or artificial intelligence to optimize asset allocation and enhance risk-adjusted returns. Compared to traditional ETFs, these thematic Smart Beta products leverage factor exposures like momentum and value while aligning with long-term macroeconomic themes, offering investors a dynamic approach to asset diversification.
Multi-Factor Rotation
Multi-factor rotation strategies within ETFs leverage dynamic allocation across various smart beta factors, such as value, momentum, and quality, to enhance risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional static smart beta funds. This tactical rotation seeks to capture factor premiums more effectively, adapting to changing market conditions and reducing drawdowns by systematically shifting exposure among multiple factors.
ESG Smart Beta
ESG Smart Beta ETFs integrate environmental, social, and governance factors with factor-based investment strategies, offering a targeted approach to sustainable asset allocation. These ETFs aim to enhance risk-adjusted returns while promoting responsible investing by combining traditional smart beta methodologies with ESG criteria.
Low Volatility ETF
Low Volatility ETFs offer investors a strategic approach to managing risk by weighting assets based on volatility metrics rather than market capitalization, enhancing portfolio stability during market downturns. Smart Beta strategies, including Low Volatility ETFs, systematically select and weight securities using factors such as volatility, providing improved risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional ETFs.
Active Smart Beta
Active Smart Beta strategies blend systematic factor-based investing with tactical active management, targeting enhanced returns and risk control compared to traditional ETFs. These strategies leverage factors like value, momentum, and low volatility while dynamically adjusting to market conditions, offering a more nuanced approach to asset allocation than passive ETFs.
Equal-Weighted ETF
Equal-weighted ETFs distribute capital evenly across all holdings, reducing concentration risk compared to market-cap-weighted smart beta strategies that overweight larger companies; this approach often leads to improved diversification and potential for enhanced long-term returns. Equal-weighted ETFs provide consistent exposure to smaller and mid-sized assets, which can offer better risk-adjusted performance in fluctuating market conditions relative to smart beta portfolios centered on factor tilts.
Dynamic Beta Allocation
Dynamic beta allocation in ETFs offers adaptive exposure to market fluctuations by continuously adjusting weights based on risk and return metrics, enhancing portfolio efficiency compared to static Smart Beta strategies. This approach leverages real-time data to optimize asset allocation, potentially improving risk-adjusted returns and reducing drawdowns in volatile market environments.
Smart Beta Rebalancing
Smart Beta rebalancing strategically adjusts asset allocations based on factor exposure and market conditions to optimize returns while mitigating risk compared to traditional ETF passive tracking. This dynamic rebalancing approach enhances portfolio efficiency by targeting specific investment biases such as value, momentum, and low volatility.
Smart Beta Indexing
Smart Beta indexing combines traditional passive ETF structures with strategic factor exposure, capturing factor premiums such as value, momentum, and low volatility to enhance risk-adjusted returns. Unlike conventional market-cap-weighted ETFs, Smart Beta funds systematically rebalance to target specific investment factors, offering a tailored approach to asset diversification and performance optimization.
ETF vs Smart Beta for asset. Infographic
 moneydiff.com
moneydiff.com